题目列表
-
跳台阶
-
变态跳台阶
-
矩形覆盖
-
二进制中1的个数
-
调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
-
链表中倒数第k个节点
-
合并两个排序的链表
-
树的子结构
-
从上到下打印二叉树
-
数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
1、跳台阶
题目描述:一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
思路分析:
对于本题,前提只有 一次 1阶或者2阶的跳法。
a.如果两种跳法,1阶或者2阶,那么假定第一次跳的是一阶,那么剩下的是n-1个台阶,跳法是f(n-1);
b.假定第一次跳的是2阶,那么剩下的是n-2个台阶,跳法是f(n-2)
c.由a\b假设可以得出总跳法为: f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2)
d.然后通过实际的情况可以得出:只有一阶的时候 f(1) = 1 ,只有两阶的时候可以有 f(2) = 2
e.可以发现最终得出的是一个斐波那契数列:
n = 1 → f(n) = 1
n = 2 → f(n) = 2
f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2) , n>2 且 n为整数
代码如下:
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
if (target <= 0) {
return -1;
} else if (target == 1) {
return 1;
} else if (target ==2) {
return 2;
} else {
return JumpFloor(target-1)+JumpFloor(target-2);
}
}
}
但是利用递归的方式效率低下,可以不利于递归,而是利用循环的方式来实现,代码如下:
int jumpFloor(int number) {
if(number<2){
return number;
}
int f1=1;
int f2=0;
int f=0;
for(int i=1;i<=number;++i)
{
f=f1+f2;
f2=f1;
f1=f;
}
return s;
}
2、变态跳台阶
题目描述:一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
思路分析:
关于本题,前提是n个台阶会有一次n阶的跳法。分析如下:
f(1) = 1
f(2) = f(2-1) + f(2-2) //f(2-2) 表示2阶一次跳2阶的次数。
f(3) = f(3-1) + f(3-2) + f(3-3)
…
f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2) + f(n-3) + … + f(n-(n-1)) + f(n-n)
说明:
(1)这里的f(n) 代表的是n个台阶有一次1,2,…n阶的 跳法数。
(2)n = 1时,只有1种跳法,f(1) = 1
(3) n = 2时,会有两个跳得方式,一次1阶或者2阶,这回归到了问题(1) ,f(2) = f(2-1) + f(2-2)
(4) n = 3时,会有三种跳得方式,1阶、2阶、3阶,
那么就是第一次跳出1阶后面剩下:f(3-1);第一次跳出2阶,剩下f(3-2);第一次3阶,那么剩下f(3-3)
因此结论是f(3) = f(3-1)+f(3-2)+f(3-3)
(5) n = n时,会有n中跳的方式,1阶、2阶…n阶,得出结论:
f(n) = f(n-1)+f(n-2)+…+f(n-(n-1)) + f(n-n) => f(0) + f(1) + f(2) + f(3) + … + f(n-1)
(6) 由以上已经是一种结论,但是为了简单,我们可以继续简化:
f(n-1) = f(0) + f(1)+f(2)+f(3) + … + f((n-1)-1) = f(0) + f(1) + f(2) + f(3) + … + f(n-2)
f(n) = f(0) + f(1) + f(2) + f(3) + … + f(n-2) + f(n-1) = f(n-1) + f(n-1)
可以得出:
f(n) = 2*f(n-1)
(7) 得出最终结论,在n阶台阶,一次有1、2、…n阶的跳的方式时,总得跳法为:
| 1 ,(n=0 )
f(n) = | 1 ,(n=1 )
| 2*f(n-1),(n>=2)
代码如下:
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloorII(int target) {
if (target <= 0) {
return -1;
} else if (target == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return 2 * JumpFloorII(target - 1);
}
}
}
同样使用递归的方式效率低下,可以采用类似“跳台阶”中的循环方式来实现。
3、矩形覆盖
题目描述:我们可以用21的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个21的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
思路分析:
依旧是斐波那契数列问题
2n的大矩形,和n个21的小矩形
其中target*2为大矩阵的大小
有以下几种情形:
(1)target <= 0 大矩形为<= 2*0,直接return 1;
(2)target = 1大矩形为2*1,只有一种摆放方法,return1;
(3)target = 2 大矩形为2*2,有两种摆放方法,return2;
(4)target = n 分为两步考虑:
第一次摆放一块 2*1 的小矩阵,则摆放方法总共为f(target - 1)

第一次摆放一块12的小矩阵,则摆放方法总共为f(target-2)。因为,摆放了一块12的小矩阵(用√√表示),对应下方的1*2(用××表示)摆放方法就确定了,所以为f(targte-2)
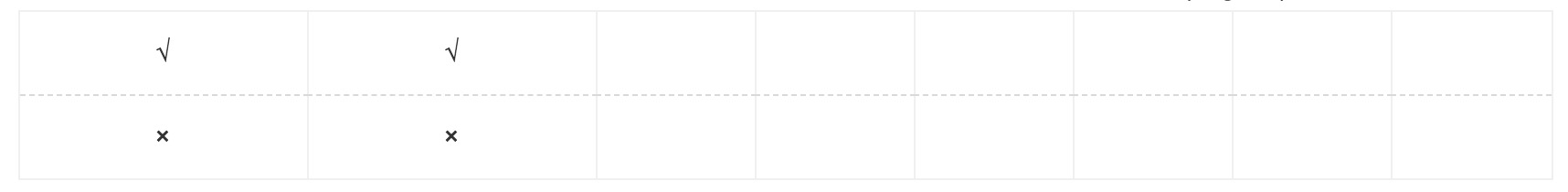
代码如下:
public class Solution {
public int RectCover(int target) {
if(target <= 1){
return 1;
}
if(target*2 == 2){
return 1;
}else if(target*2 == 4){
return 2;
}else{
return RectCover((target-1))+RectCover(target-2);
}
}
}
## 4、二进制中1的个数 题目描述:输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
思路分析[【1】:用1逐个左移然后与输入进行“与”操作,如果与的结果不为0,则说明1对应的位数为1,否则为0。
代码【1】:
public static int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count = 0;
int flag = 1;
while (flag != 0) {
if ((n & flag) != 0) {
count++;
}
flag = flag << 1;
}
return count;
}
思路分析【2】:如果一个整数不为0,那么这个整数至少有一位是1。如果我们把这个整数减1,那么原来处在整数最右边的1就会变为0,原来在1后面的所有的0都会变成1(如果最右边的1后面还有0的话)。其余所有位将不会受到影响。
举个例子:一个二进制数1100,从右边数起第三位是处于最右边的一个1。减去1后,第三位变成0,它后面的两位0变成了1,而前面的1保持不变,因此得到的结果是1011。我们发现减1的结果是把最右边的一个1开始的所有位都取反了。这个时候如果我们再把原来的整数和减去1之后的结果做与运算,从原来整数最右边一个1那一位开始所有位都会变成0。如1100&1011=1000.也就是说,把一个整数减去1,再和原整数做与运算,会把该整数最右边一个1变成0。那么一个整数的二进制有多少个1,就可以进行多少次这样的操作。
代码【2】:
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count = 0;
while(n!= 0){
count++;
n = n & (n - 1);
}
return count;
}
5、调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题目描述:输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
思路分析【1】:类似冒泡排序原理,前后比较,如果前偶后奇则进行交换位置,时间复杂度为O(n^2)
代码如下:
public class Solution {
public void reOrderArray(int [] array) {
for(int i= 0;i<array.length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<array.length-1-i;j++){
if(array[j]%2==0&&array[j+1]%2==1){
int t = array[j];
array[j]=array[j+1];
array[j+1]=t;
}
}
}
}
}
思路分析【2】:要想保证原有次序,则只能顺次移动或相邻交换。
(1)i从左开始向右边遍历,找到第一个偶数
(2)j从i+1开始向右边开始遍历,找到第一个奇数
(3)将数组的[i,i+1,i+2,……,j-1]位置的元素向右边移动一位,然后将找到的第一个奇数放到i的位置,即右移前下标为j的元素放置到下标为i的位置,然后i++
(4)终止条件为:j向后遍历失败
代码如下:
public void reOrderArray2(int [] a) {
if(a==null||a.length==0){
return;
}
int i = 0,j;
while(i<a.length){
while(i<a.length&&!isEven(a[i])){
i++;
}
j = i+1;
while(j<a.length&&isEven(a[j])){
j++;
}
if(j<a.length){
int tmp = a[j];
for (int j2 = j-1; j2 >=i; j2--) {
a[j2+1] = a[j2];
}
a[i++] = tmp;
}else{// 查找失敗
break;
}
}
}
boolean isEven(int n){
if(n%2==0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
6、链表中倒数第k个节点
题目描述:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
思路分析【1】:定义两个指针,让两个指针的距离为k步,即先让第一个指针和第二个指针都指向头结点,然后再让第一个指正走(k-1)步,到达第k个节点。然后两个指针同时往后移动,当第一个结点到达末尾的时候,第二个结点所在位置就是倒数第k个节点了。
代码如下:
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head==null||k<=0){
return null;
}
ListNode pre=head;
ListNode last=head;
for(int i=1;i<k;i++){
if(pre.next!=null){
pre=pre.next;
}else{
return null;
}
}
while(pre.next!=null){
pre = pre.next;
last = last.next;
}
return last;
}
}
思路分析【2】:遍历链表,计算链表长度length,若长度length小于k则返回null;知道length后,再继续遍历链表,遍历的第length-k+1步即为倒数第k个元素。
代码如下:
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode tempNode = head;
int length = 1;
while (head.next != null) {
length++;
head = head.next;
}
if (length < k) {
return null;
}
for (int i = 0; i < length - k; i++) {
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
return tempNode;
}
7、合并两个排序的链表
题目描述:输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
// 非递归实现
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
//新建一个头节点,用来存合并的链表。
ListNode head=new ListNode(-1);
head.next=null;
ListNode root=head;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val < list2.val){
head.next = list1;
head = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
head.next = list2;
head = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
//把未结束的链表连接到合并后的链表尾部
if(list1 != null){
head.next = list1;
}
if(list2 != null){
head.next = list2;
}
return root.next;
}
}
// 递归实现
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}else if(list2==null){
return list1;
}
ListNode pMergeHead = null;
if(list1.val<list2.val){
pMergeHead = list1;
pMergeHead.next = Merge(list1.next,list2);
}else{
pMergeHead = list2;
pMergeHead.next = Merge(list1,list2.next);
}
return pMergeHead;
}
}
8、树的子结构
题目描述:输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
代码如下:
public class Solution {
public static boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
boolean result = false;
//当Tree1和Tree2都不为零的时候,才进行比较。否则直接返回false
if (root2 != null && root1 != null) {
//如果找到了对应Tree2的根节点的点
if(root1.val == root2.val){
//以这个根节点为为起点判断是否包含Tree2
result = doesTree1HaveTree2(root1,root2);
}
//如果找不到,那么就再去root的左儿子当作起点,去判断时候包含Tree2
if (!result) {
result = HasSubtree(root1.left,root2);
}
//如果还找不到,那么就再去root的右儿子当作起点,去判断时候包含Tree2
if (!result) {
result = HasSubtree(root1.right,root2);
}
}
//返回结果
return result;
}
public static boolean doesTree1HaveTree2(TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2) {
//如果Tree2已经遍历完了都能对应的上,返回true
if (node2 == null) {
return true;
}
//如果Tree2还没有遍历完,Tree1却遍历完了。返回false
if (node1 == null) {
return false;
}
//如果其中有一个点没有对应上,返回false
if (node1.val != node2.val) {
return false;
}
//如果根节点对应的上,那么就分别去子节点里面匹配
return doesTree1HaveTree2(node1.left,node2.left) && doesTree1HaveTree2(node1.right,node2.right);
}
9、从上到下打印二叉树
题目描述:从上往下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同层节点从左至右打印。
分析:二叉树的层序遍历,借助一个队列即可
代码如下:
public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root==null){
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode tempNode = queue.poll();
if(tempNode.left!=null) {
queue.offer(tempNode.left);
}
if(tempNode.right!=null) {
queue.offer(tempNode.right);
}
list.add(tempNode.val);
}
return list;
}
10、数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
题目描述:数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例如输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。如果不存在则输出0。
分析;若存在这么一个数,那么这个数字一定在排序好后的数组的最中间位置
代码如下:
public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int[] array) {
if (array.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
if(array.length == 1) {
return array[0];
}
Arrays.sort(array);
int result = array[(array.length / 2) + 1];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] == result) {
count++;
}
}
return count >= (array.length / 2) + 1 ? result : 0;
}